Weighing the Pros and Cons of PostgreSQL and MySQL for Developers

Choosing between PostgreSQL vs MySQL presents a real challenge for developers. PostgreSQL offers advanced features and standards compliance, while MySQL stands out for speed and ease of use. The right database can boost your project’s performance, scalability, and data consistency. Recent statistics show PostgreSQL leads in developer usage:
Database | Usage Percentage (2025) |
|---|---|
PostgreSQL | |
MySQL | 41.09% |
Your decision should align with your workload, data type, and business needs. Chat2DB supports both databases, making it simple to explore the pros and cons of PostgreSQL vs MySQL in your projects.
Key Takeaways
PostgreSQL offers advanced features, strong data integrity, and supports complex data types, making it ideal for projects needing flexibility and reliability.
MySQL focuses on speed, ease of use, and quick deployment, fitting well with web applications and projects that prioritize simplicity and performance.
PostgreSQL excels in handling high concurrency and complex queries, while MySQL performs best in read-heavy workloads with moderate write demands.
Choosing the right database depends on your project needs, such as data complexity, scalability, and compliance requirements.
Tools like Chat2DB help manage both PostgreSQL and MySQL easily, even without deep SQL knowledge, boosting productivity and simplifying database tasks.
Overview
What is PostgreSQL?
You will find PostgreSQL stands out as an object-relational database management system. This open-source database combines advanced features with strict standards compliance. PostgreSQL supports custom data types, procedural languages, and user-defined functions. You can model complex real-world data using table inheritance and specialized data types. Its process-based architecture isolates client connections, which enhances stability. PostgreSQL uses Multi-Version Concurrency Control (MVCC) for high concurrency and robust ACID compliance. You can create custom types and leverage advanced indexing methods like GIN, GiST, and BRIN. These features make PostgreSQL a top choice for developers who need flexibility and reliability in their database management system.
What is MySQL?
MySQL is a relational database management system designed for speed, reliability, and ease of use. As an open-source version, MySQL powers many web applications and enterprise systems. You benefit from a modular client-server architecture that scales from small projects to large deployments. MySQL supports multiple storage engines, with InnoDB providing transactional support, row-level locking, and crash recovery. The database enforces data integrity through primary and foreign keys. MySQL offers a query optimizer, advanced indexing, and partitioning to boost performance. You can rely on its robust security features, including SSL/TLS encryption and role-based access control. MySQL’s design philosophy focuses on delivering a fast, stable, and developer-friendly dbms.
Aspect | PostgreSQL | MySQL |
|---|---|---|
Object-relational model with table inheritance, specialized data types, and functions as data features | Purely relational model focused on simple table schemas and foreign keys | |
Concurrency Control | InnoDB engine with row-level locking | |
Extensibility | Advanced indexing and custom functions/data types | Simpler indexing and limited extensibility |
Replication | WAL-based replication for scalable, fine-grained read replicas | Third-party tools or InnoDB cluster for high availability |
Security Features | Robust native encryption and row-level security | Less comprehensive native encryption and row-level security |
Community and Popularity
You will notice both PostgreSQL and MySQL enjoy extensive community support. These open-source databases rank as the most popular relational database management systems worldwide. According to recent surveys, PostgreSQL has become the most admired open-source database among developers, with 45.5% choosing it as their top option. MySQL remains a close second, trusted for its speed and simplicity. This popularity reflects the reliability, flexibility, and broad applicability of both databases.
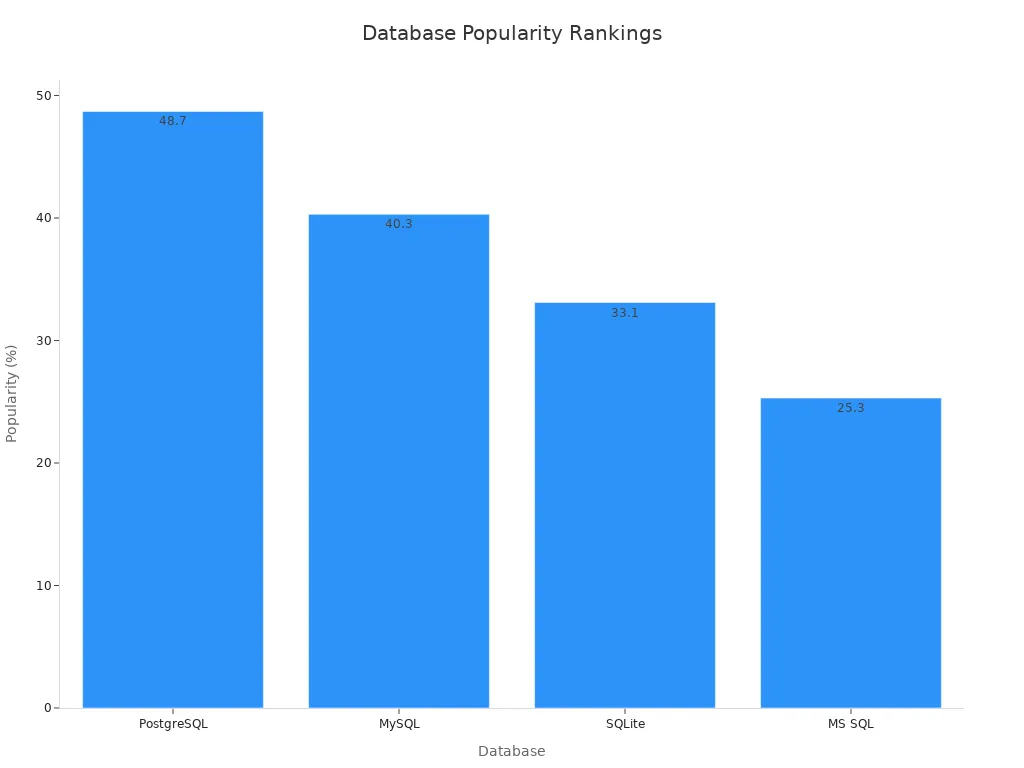
PostgreSQL vs MySQL
Features Comparison
When you compare postgresql vs mysql, you see clear core differences in their features and flexibility. PostgreSQL stands out as a feature-rich database with advanced features that support a wide range of data types, including JSONB, arrays, hstore, and geometric types. You can define custom functions in multiple languages, create complex queries, and use materialized views. PostgreSQL’s extensibility lets you build custom operators and index types, giving you unmatched flexibility for complex transactions and data relationships.
MySQL, on the other hand, focuses on simplicity and speed. It supports standard SQL data types and offers strong community and enterprise support. You will find MySQL easier to deploy and manage for web applications that do not require advanced features or customization. Its stored procedures are primarily SQL-based, and triggers are limited to row-level, which restricts some functionality compared to PostgreSQL.
PostgreSQL supports advanced data types and custom functions.
MySQL emphasizes ease of use and fast deployment.
PostgreSQL offers comprehensive triggers and procedural languages.
MySQL provides reliable performance for simpler applications.
Performance
Performance is a key factor in the postgresql vs mysql debate. PostgreSQL uses Multi-Version Concurrency Control (MVCC) to deliver strong concurrency and full acid compliance. This approach allows multiple users to read and write data at the same time without locking, which boosts scalability and consistency in high-concurrency environments. Benchmarks show PostgreSQL outperforms MySQL in overall speed, read, and write performance, especially for write-heavy workloads and complex queries.
Metric | PostgreSQL Performance | MySQL Performance | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|
Overall Speed | Baseline | Sysbench latency tests | |
Read Performance | ~60% faster | Baseline | Read benchmark tests |
Write Performance | ~3.5x faster | Baseline | Write benchmark tests |
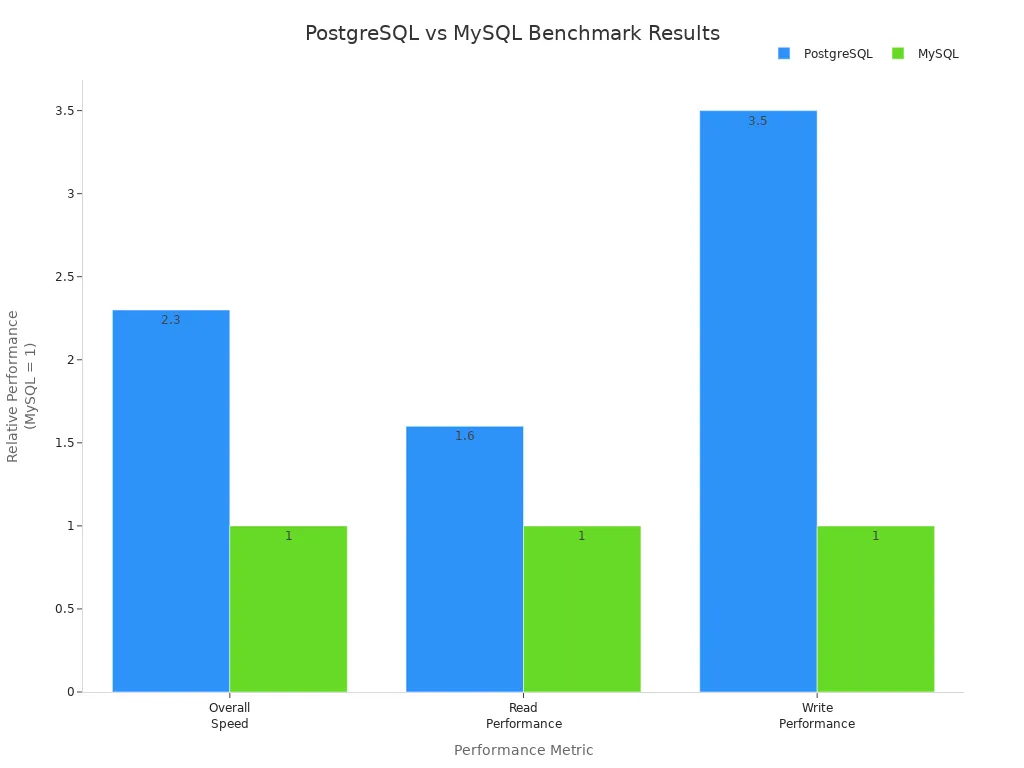
MySQL performs well for read-heavy web applications and offers reliable performance for moderate write concurrency. However, under heavy write loads, its concurrency control is less robust than PostgreSQL’s.
Standards and Compliance
You will notice core differences in standards compliance between these two relational database management systems. PostgreSQL is known for its full acid compliance and strict adherence to SQL standards. This makes it ideal for industries that require data integrity and complex transactions, such as finance or scientific research. PostgreSQL supports advanced features like check constraints and sophisticated access control, ensuring strong concurrency control and transactional robustness.
MySQL, while supporting acid compliance through InnoDB, only partially follows ANSI SQL standards. It prioritizes usability and speed, sometimes at the expense of strict standards. For projects where compliance and data integrity are critical, PostgreSQL is the preferred dbms. For simpler, high-speed deployments, MySQL remains a popular open-source choice.
Pros and Cons
PostgreSQL Pros and Cons
When you evaluate PostgreSQL, you discover a database that excels in reliability, flexibility, and advanced features. Developers often choose PostgreSQL for projects that demand strict standards compliance and robust data integrity. Here are the main advantages you will experience:
You benefit from extensive support for SQL features and standards, with about 95% compliance with SQL:2016.
You can work with a wide range of data types, including JSON, XML, key-value, and even graph extensions, which increases flexibility for complex applications.
You gain access to broad programming language support, both server-side and through external languages, such as C/C++, Java, Python, and Perl.
You can process bulk data efficiently using table partitioning, parallel queries, and advanced analytic functions.
You receive strong open-source community support, with comprehensive documentation, books, and active forums.
You save on costs because PostgreSQL is open-source, allowing free use, modification, and redistribution.
You enjoy fast and flexible development, driven by a global community that shares technical solutions.
You achieve high reliability and stability, thanks to a large, active developer base worldwide.
You can rely on ACID compliance and transactional integrity for mission-critical workloads.
You benefit from cross-platform compatibility, supporting UNIX, MacOS, Windows, and Linux.
Tip: PostgreSQL’s reliability and advanced features make it a top choice for applications that require complex data models and high concurrency.
However, you should also consider the disadvantages:
PostgreSQL requires a more complex setup and ongoing maintenance, which can challenge new users.
You may need skilled database administrators for tuning, monitoring, and managing backups.
Native horizontal scaling is limited, so you must use additional tools like Citus or pgpool for large-scale deployments.
Extra configurations and specialized knowledge increase deployment complexity and maintenance costs.
Scaling PostgreSQL for massive workloads often demands investment in experienced personnel or external support.
MySQL Pros and Cons
MySQL remains a popular choice for developers who value speed, reliability, and ease of use. You will find it especially effective for web applications and projects that need quick deployment. Here are the main advantages:
You benefit from strong data security, with MySQL recognized for its reliability and safety in handling both informational and transactional data.
You can scale on demand, managing large data volumes and customizing the database for applications like e-commerce.
You experience high performance, as MySQL’s storage-engine framework ensures smooth operation even under heavy query loads.
You gain superior workflow control, with quick installation, cross-platform compatibility, and self-management features that automate administration.
You receive adequate transactional support, meeting the needs of most developers.
You enjoy the reliability of a mature, open-source platform trusted by millions worldwide.
Note: MySQL’s reliability and performance make it ideal for projects that require fast, stable, and straightforward database solutions.
Still, you should weigh the disadvantages:
MySQL faces scalability challenges with very large datasets, especially for write-heavy environments, often requiring complex sharding solutions.
You may find it difficult to implement advanced features or complex transactions, which can slow development for analytical or financial applications.
Performance tuning can be challenging and may require deep expertise to optimize for high-traffic scenarios.
Built-in full-text search capabilities are limited, which can affect search-heavy applications.
Replication lag and complexity can cause data inconsistency during peak updates.
Some users express concerns about the pace of development since Oracle’s acquisition, which may impact future features.
Debugging stored procedures and triggers can be difficult due to limited tools.
Strict schema requirements reduce flexibility when adapting to changing data needs.
Potential vendor lock-in and licensing model nuances may complicate proprietary software distribution.
Use Cases

When to Choose PostgreSQL
You should select PostgreSQL when your project demands advanced data modeling, strict standards compliance, or high reliability. PostgreSQL excels in scenarios where you need to handle complex data types, perform analytical queries, or ensure transactional integrity. Its support for JSON, arrays, and geospatial data makes it ideal for applications that require flexibility and scalability. You can rely on PostgreSQL for industries that prioritize data integrity and security, such as finance, healthcare, and government.
Key Benefits and Features of PostgreSQL | |
|---|---|
Content Management Systems (CMS) | Flexible handling of semi-structured content, full-text search, and text analysis |
Data Warehousing | Support for transactional and analytical workloads, materialized views, and partitioning |
Geographic Information Systems | Advanced geospatial data support with PostGIS extension |
E-commerce | Reliable transaction handling and scalability for high-volume orders |
Financial Services | ACID compliance and secure transaction processing |
Healthcare | Data integrity, security, and compliance |
Scientific Research | Handling complex datasets and advanced analytics |
Tip: Choose PostgreSQL if your application requires advanced features, high reliability, and the ability to scale for complex or high-volume workloads.
When to Choose MySQL
You should consider MySQL for projects that need fast deployment, ease of use, and proven reliability. MySQL works well for web applications, eCommerce platforms, and SaaS products where speed and straightforward management matter most. Its architecture supports high-performance analytics and transaction processing, making it suitable for online gaming, retail POS systems, and educational platforms. MySQL’s broad compatibility and robust security features help you maintain data integrity while scaling to meet growing user demands.
MySQL fits projects with high read loads and moderate write concurrency.
You benefit from simple installation and user-friendly management tools.
MySQL supports enterprise-grade applications in finance, broadcasting, and digital banking.
Its cost-effectiveness and cross-platform compatibility make it a practical choice for many developers.
Note: MySQL’s reliability and performance make it a strong option for applications that prioritize speed, cost efficiency, and ease of management.
Chat2DB for Both Databases
Chat2DB empowers you to manage both PostgreSQL and MySQL databases from a single, intuitive platform. You can connect to multiple databases, explore schemas visually, and generate SQL queries using natural language. The AI-powered SQL generator and Text2SQL features allow you to interact with your database without deep SQL expertise. You gain access to real-time dashboards, automated data analysis, and seamless data migration tools, all designed to boost productivity and reduce complexity.
Chat2DB supports centralized management of diverse databases, enhancing reliability and scalability.
You can collaborate securely with your team, share dashboards, and audit SQL activity for compliance.
The platform’s advanced security measures, including encryption and local data processing, protect your sensitive information.
Chat2DB’s cross-platform accessibility ensures you can work efficiently, whether on desktop, web, or Docker.
With Chat2DB, you streamline database management, accelerate development, and ensure reliability across all your projects.
You have seen that PostgreSQL delivers advanced features, strong data integrity, and high scalability, while MySQL stands out for simplicity, speed, and a vast ecosystem.
PostgreSQL supports complex data types, custom functions, and robust transaction handling.
MySQL excels in read-heavy workloads and quick setup, making it ideal for straightforward projects.
Your project’s needs and your team’s priorities should guide your choice. With Chat2DB, you can easily explore, manage, and compare both databases.
Share your experiences or questions below—your insights help the community grow!
FAQ
What database should you choose for complex analytics?
You should choose PostgreSQL. It supports advanced data types, custom functions, and powerful analytic features. PostgreSQL handles complex queries and large datasets efficiently.
Can you migrate data between PostgreSQL and MySQL easily?
Yes, you can migrate data between PostgreSQL and MySQL. Chat2DB provides tools for seamless schema and data migration. You can handle millions of rows and multiple file formats with minimal effort.
Does Chat2DB require deep SQL knowledge?
You do not need deep SQL knowledge to use Chat2DB. Its AI-powered SQL generator and Text2SQL features let you write queries in plain English. The platform creates accurate SQL statements for you.
Is it safe to manage sensitive data with Chat2DB?
Chat2DB uses local query processing.
Your schema never uploads to the cloud.
The platform applies AES and RSA encryption for data storage and transmission.
You can trust Chat2DB to protect sensitive information.
See Also
Key Factors To Consider When Picking MySQL Or PostgreSQL
Comparing Psql, Mysql, And Sqlcmd For Best Command Line Use
Evaluating Chat2DB Against Classic SQL Tools For Efficiency

